Understanding Idiopathic Urticaria: Symptoms and Insights

Intro
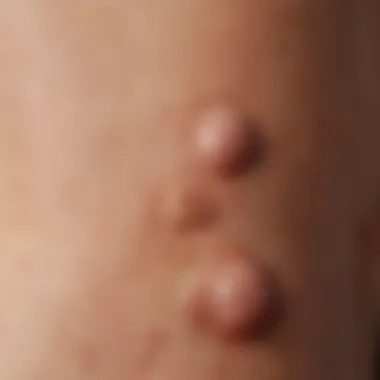
Idiopathic urticaria is a condition that affects a significant number of individuals. It manifests as hives, welts, or wheals on the skin, varying in size and often accompanied by itching. The mysterious nature of idiopathic urticaria can complicate both diagnosis and treatment, making a clear understanding essential. This article aims to delve into the symptoms associated with idiopathic urticaria and explore insights that shed light on this often perplexing dermatological issue.
Research Overview
Summary of Key Findings
Recent studies underscore that idiopathic urticaria can sometimes be triggered by multiple factors, though a specific cause is often elusive. Several key findings emerge from current research:
- Common Symptoms: Itching, skin redness, and raised hives are frequently reported.
- Potential Triggers: Stress, infections, medication, and certain foods may play a role.
- Diagnosis Complexity: Many patients do not provide a clear history of allergic reactions, making evaluation difficult.
- Management Strategies: Tailored treatment can include antihistamines, corticosteroids, or other immunomodulators.
Background and Context
The prevalence of idiopathic urticaria contributes to its significance in dermatology. While it is a common ailment, the broad spectrum of symptoms and their unpredictable nature presents challenges for healthcare professionals. Understanding this condition requires not only recognition of the clinical features but also an awareness of the lifestyle and environmental factors that may influence its occurrence.
Symptoms of Idiopathic Urticaria
Idiopathic urticaria is characterized by several symptoms, which can vary in presentation:
- Hives/Papules: Raised areas on the skin, which can be red, itchy, and painful.
- Angioedema: Deeper swelling that often affects the face and throat, potentially obstructing airways.
- Erythema: Red patches that can appear on various parts of the body, indicating irritation.
Patients might also experience chronic symptoms lasting more than six weeks, making the condition persistent and debilitating.
Insights into Triggers and Diagnosis
Identifying Triggers
Understanding possible triggers can aid in managing idiopathic urticaria. Common triggers include:
- Emotional stress
- Physical stimuli, such as heat or cold
- Certain food items, like nuts or shellfish
- Alcohol and caffeine
By maintaining a symptom diary, patients can help identify these triggers, facilitating discussions with their healthcare provider.
Diagnostic Approaches
The diagnostic procedures may involve:
- Clinical Evaluation: A detailed medical history and physical examination.
- Allergy Testing: Skin or blood tests to rule out specific allergies.
- Provocation Tests: Controlled exposure to potential triggers under medical supervision.
These approaches help determine the underlying factors contributing to symptoms and guide appropriate management.
Management Strategies
Effective management may require a multifaceted approach, including:
- Antihistamines: These medications can alleviate symptoms for many patients.
- Corticosteroids: For severe cases, short courses may be prescribed to reduce inflammation.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Stress reduction techniques can be beneficial.
Patients should collaborate with their healthcare provider to tailor strategies based on their unique presentation and needs.
"Idiopathic urticaria, while common, remains an enigma that underscores the necessity for ongoing research and refined therapeutic protocols."
The End
Intro to Idiopathic Urticaria
Idiopathic urticaria, a dermatological enigma, can profoundly impact the lives of those afficted. Recognizing its symptoms and triggers is crucial for comprehensive management. This section lays the groundwork by establishing a clear understanding of what idiopathic urticaria is and its significance in clinical practice.
Definition and Background
Idiopathic urticaria refers to a skin condition characterized by hives - raised, itchy welts that may appear suddenly and can vary in size. The term "idiopathic" indicates that the precise cause remains unknown despite thorough investigation. This absence of clarity can lead to frustration for both patients and healthcare providers. It often emerges without any identifiable cause, making it a perplexing condition to diagnose and manage.


Understanding the background of idiopathic urticaria involves recognizing its potential links to systemic responses, including immune system activities. Those afflicted might experience episodes that last from minutes to days, with symptoms sometimes reemerging unpredictably. Due to its nature, it often creates anxiety in patients, leading many to seek extensive medical advice.
Epidemiology of Idiopathic Urticaria
Idiopathic urticaria is relatively common, with studies estimating that it affects approximately 1% to 3% of the population at some point in their lives. It can occur in individuals of any age, although it often presents most prominently in young adults. There is also evidence to suggest that idiopathic urticaria may have a slight female predominance, with women appearing more frequently in case studies and treatment populations.
Several factors contribute to the epidemiology of this condition. Demographics, lifestyle, and environmental influences play essential roles. For instance, certain geographical regions may report different prevalence rates due to variations in allergens or climate conditions. Additionally, chronic stress has been implicated in exacerbating symptoms, illustrating the multifaceted nature of this ailment. That is why understanding the epidemiological aspects is vital in developing effective prevention and treatment strategies.
"Idiopathic urticaria is not only a skin condition; it reflects underlying physiological processes that can be intricate and multifarious."
Fundamental Symptoms of Idiopathic Urticaria
The study of fundamental symptoms in idiopathic urticaria allows for a better understanding of this complex condition. Identifying these symptoms is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers. Symptoms provide a roadmap for recognizing and diagnosing idiopathic urticaria, ensuring timely intervention and effective treatment plans. Understanding the characteristics of these symptoms can also guide research and foster better patient communication.
Common Physical Manifestations
The common physical manifestations of idiopathic urticaria include a range of symptoms that can significantly affect a person's quality of life. Three major aspects stand out—itching and discomfort, swelling of affected areas, and redness along with rash appearance.
Itching and Discomfort
Itching and discomfort represent one of the most prominent symptoms of idiopathic urticaria. This sensation can be severe and persistent, leading to an urgent need for relief. Patients may experience intense itching even when no visible rash is present. The importance of this symptom cannot be overstated; it often drives individuals to seek medical attention.
One characteristic of itching is its unpredictable intensity. It may fluctuate throughout the day, causing frustration for patients. This symptom is beneficial for this article because it highlights the urgent need for effective treatment options tailored to alleviate discomfort.
Swelling of Affected Areas
Swelling of affected areas generally occurs in conjunction with itching. The swelling, or angioedema, typically appears suddenly and can vary in size. This condition can be alarming, as it may affect the face, lips, eyes, and even the throat. Understanding this symptom is vital, as severe swelling can lead to complications requiring immediate medical intervention. The notable feature of this swelling is its rapid onset, which differentiates it from other allergic reactions. In this article, swelling is an important focus due to its potential to escalate in severity, impacting both treatment decisions and patient safety.
Redness and Rash Appearance
Redness and rash appearance complete the trio of common physical manifestations. Affected areas may present with welts or hives that are often raised and red. This symptom can vary in size and shape, further complicating diagnosis. The significance of redness and rash appearance is apparent, as these visible signs can help healthcare providers determine the underlying cause of the urticaria. Additionally, the transient nature of these rashes makes them intriguing, as they can disappear as quickly as they appear. Addressing this symptom in the article aids in building awareness and understanding among readers who may encounter idiopathic urticaria in clinical or personal settings.
Duration and Cyclic Nature
The duration and cyclic nature of idiopathic urticaria symptoms present another dimension to the disorder. Symptoms may last for a few hours or several days, but they often recur unpredictably. This variability presents challenges in managing the condition. Patients frequently report that symptoms can subside only to return later, sometimes triggered by environmental factors or emotional states. Understanding these patterns provides insights into how patients can best cope, guiding preventive measures. Recognizing that symptoms can vary in duration and pattern is key to formulating comprehensive management strategies.
Variability in Symptoms
The concept of variability in symptoms is paramount when delving into idiopathic urticaria. Understanding this variability helps both patients and healthcare providers navigate the unpredictable nature of this condition. Idiopathic urticaria can manifest distinctly from one individual to another, making it essential to recognize that symptoms may not follow a consistent pattern. This variability can affect the experience of the condition and influence management strategies.
Key elements include recognizing that symptoms can fluctuate based on numerous factors such as time of day, stress levels, and environmental changes. Awareness of these elements provides insight into how treatment approaches might need to be tailored to individual patient needs.
Considerations about variability also emphasize the need for ongoing dialogue between patients and healthcare practitioners. By discussing observed patterns or triggers, patients can contribute valuable information that aids in optimizing treatment plans.
Atypical Symptoms in Patients
Atypical symptoms can emerge in patients suffering from idiopathic urticaria. These symptoms can deviate from the standard manifestations of itching, redness, and swelling. For example, some patients may experience gastrointestinal symptoms or fatigue alongside the typical skin symptoms. This atypical manifestation complicates the diagnosis and management of the condition. It highlights the importance of comprehensive evaluations and patient histories during clinical assessments.
These unusual presentations demand a more thoughtful consideration of treatment options, as they can suggest additional underlying issues. Understanding atypical symptoms is crucial for forming effective management strategies that address the full scope of the patient’s experience.
Symptom Fluctuation and Triggers
Symptom fluctuation is a common aspect of idiopathic urticaria, often influenced by various triggers. Recognizing these triggers can provide clarity for both patients and practitioners in managing the condition effectively.
Stress-related Symptoms
Stress-related symptoms are significant in understanding idiopathic urticaria. Stress can profoundly impact the skin, resulting in flare-ups of hives or angioedema. The key characteristic of stress-related symptoms is their immediate correlation to emotional and psychological states. These symptoms present a unique challenge for management since addressing emotional health can sometimes be as critical as treating physical symptoms.
However, this can lead to a beneficial perspective that emphasizes holistic care, allowing patients to explore varied coping mechanisms to reduce overall stress levels effectively.
Temperature Changes
Temperature changes significantly contribute to the symptoms of idiopathic urticaria. Rapid shifts in temperature, such as a sudden increase in heat or cold, can trigger flare-ups. The primary characteristic here is the body’s reaction to environmental conditions. Some patients might find relief in cooler environments, while others may react adversely to high temperatures.


The unique feature of temperature changes as a trigger necessitates patient education on environmental awareness, allowing individuals to adapt their settings according to their sensitivity. However, this can also limit daily activities, serving as a disadvantage to those affected.
Environmental Allergens
Environmental allergens, ranging from pollen to dust mites, are notable triggers for idiopathic urticaria. These allergens can provoke allergic reactions that exacerbate existing skin conditions. The explicit characteristic of environmental allergens is their ubiquitous presence, which can make avoidance challenging for patients.
The unique feature of assessing environmental allergens can lead to effective allergy management strategies such as immunotherapy or allergen avoidance. However, constantly addressing these allergens can be burdensome, creating an additional layer of complexity for individuals managing their symptoms.
Potential Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding the potential causes and risk factors of idiopathic urticaria is crucial. This knowledge aids in identifying patterns and tailoring treatment effectively. By comprehending what influences the onset and severity of symptoms, healthcare professionals and patients can work collaboratively towards better management strategies.
Factors contributing to idiopathic urticaria can be manifold. They may include genetic elements, autoimmune response, environmental triggers, and individual lifestyle choices. A detailed examination of these components enhances the ability to formulate effective coping mechanisms and treatment plans. Delving into these areas can illuminate the complexities involved, offering new insights and avenues for future research.
Genetic Predisposition
Genetic predisposition appears to play a significant role in idiopathic urticaria. It suggests that some individuals may have an inherited tendency to develop this condition. Family history can be a marker for risk, indicating that if a relative has experienced chronic urticaria, other family members might also be at elevated risk.
Research indicates that certain genetic markers may correlate with the occurrence of urticaria. Variations in the immune system, especially those influencing histamine release, could lead to heightened probabilities of experiencing symptoms. Additionally, conditions such as angioedema, which can accompany urticaria, show familial patterns, reinforcing the genetic link.
Autoimmune Considerations
Autoimmune considerations are another essential factor in understanding idiopathic urticaria. In this context, the body's immune system mistakenly attacks its own cells, leading to exaggerated responses such as skin rashes and swelling. This miscalibrated immune response may involve the production of autoantibodies that target mast cells, which are pivotal in the allergic response.
Some individuals with idiopathic urticaria display underlying autoimmune disorders, such as lupus or thyroid disease. This connection raises important questions about the diagnostic process, compelling further examination into the presence of autoimmune factors among patients.
In summary, knowledge of genetic predisposition and autoimmune considerations enhances comprehension of idiopathic urticaria. Understanding these potential causes can facilitate timely diagnosis and support targeted treatment approaches, greatly benefiting patient outcomes.
Diagnostic Processes
Diagnostic processes play a vital role in understanding idiopathic urticaria. Correct diagnosis can help in identifying and managing this enigmatic skin condition. Various approaches are employed, each contributing distinct information. These methods allow healthcare providers to differentiate idiopathic urticaria from similar dermatological issues, leading to more effective treatment strategies.
Clinical Evaluation Approaches
Clinical evaluation begins with a thorough patient history. Doctors inquire about symptom patterns, triggers, and duration. Detailed information allows for an informed assessment. Physical examination follows, where clinicians examine skin lesions and any accompanying symptoms. Identifying the characteristic wheals or hives is crucial.
Health professionals often consider medical history, allergies, and family history as potential influencing factors. Understanding these dimensions may reveal insights into possible underlying causes. This holistic approach aids in creating a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to individual needs.
Additionally, patient diaries may be recommended. Keeping track of flare-ups, environmental exposures, and lifestyle factors can enhance the evaluation process substantially. Such records can pinpoint triggers, leading to personalized care.
Additional Laboratory Tests
Sometimes, clinical evaluation alone is insufficient. In such situations, laboratory tests provide needed clarity. Two primary tests include blood tests and skin allergy testing.
Blood Tests
Blood tests serve as a common diagnostic tool in assessing idiopathic urticaria. They help rule out systemic conditions or autoimmune disorders. The key characteristic of blood tests is their ability to evaluate various elements like eosinophil counts or markers of inflammation. These factors help clinicians understand the extent of the condition.
The beneficial aspect of blood tests is their non-invasive nature and ability to provide a quick overview of the patient’s overall health. However, a unique feature is the limitation of blood tests in directly diagnosing idiopathic urticaria. They can only provide supportive evidence rather than definitive answers.
Skin Allergy Testing
Skin allergy testing is another important diagnostic procedure. This method identifies specific allergens that may contribute to urticaria. The key characteristic is its capacity to pinpoint immediate allergic reactions.
Skin testing is a popular choice for practitioners because it offers direct results. The unique feature is its specificity in identifying triggers. Results can inform the patient about potential allergens to avoid. However, some disadvantages exist; skin tests may lead to false positives or may not capture delayed allergic responses. This limitation indicates the need for a comprehensive evaluation including clinical history and patient input.
Through understanding these diagnostic processes, practitioners can create a pathway for better management of idiopathic urticaria. Early and precise diagnosis is essential for improving patient outcomes.
Management and Treatment Strategies
Managing idiopathic urticaria effectively is crucial for improving patient quality of life. This condition often leads to significant discomfort and emotional distress. Therefore, understanding the various management techniques can help both patients and healthcare providers make informed decisions. Treatment strategies often involve a combination of pharmacological interventions and lifestyle adjustments. Addressing symptoms as they arise is particularly important, as it can prevent further complications and improve daily functioning.


First-line Treatment Options
Antihistamines
Antihistamines are commonly regarded as the first line of defense in treating idiopathic urticaria. They work by blocking histamine receptors, which reduces itching and other acute symptoms associated with this condition. The key characteristic of antihistamines is their rapid onset of action, often providing relief within a few hours.
These medications are not only popular but also widely prescribed due to their relative safety and effectiveness. Some common antihistamines include cetirizine and loratadine, which are known for causing minimal sedation compared to older generation antihistamines.
However, there are unique considerations regarding antihistamines. Some patients may experience side effects such as drowsiness or gastrointestinal disturbances. This can impact compliance with the treatment regimen and consequently prolong symptomatology. Regular consultation with healthcare providers is advisable to ensure optimal medication choices based on individual responses.
Topical Corticosteroids
Topical corticosteroids also play a role in managing idiopathic urticaria, especially in localized cases. These anti-inflammatory medications help in reducing redness and swelling in the affected areas, thus providing symptomatic relief. The key characteristic of topical corticosteroids is their potency. They can vary significantly, allowing tailored treatments suited for different severities of the condition.
Topical corticosteroids are especially beneficial due to their localized action, which reduces the potential for systemic side effects associated with oral steroids. However, prolonged use can lead to skin thinning, a unique feature that demands cautious application. Regular follow-up while using topical corticosteroids is essential to monitor for any emerging side effects.
Long-term Management Considerations
When considering long-term management for idiopathic urticaria, a holistic approach is vital. It often entails not just medication, but also educational efforts for both patients and families. Recognizing triggers and adopting avoidance strategies can empower patients and enhance their coping abilities.
In addition, patients may benefit from therapy focused on stress management and lifestyle modification, which complement medical treatments. Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers can help adjust treatment plans as needed, ensuring continued effectiveness over time. Close monitoring is fundamental in adapting treatment strategies to changing patient needs, minimizing the impact of this complex condition on daily living.
Patient Perspectives and Experiences
Understanding the experiences of patients with idiopathic urticaria is critical. This section provides insight into how this condition affects daily life. Patient perspectives illuminate the complexities beyond clinical symptoms. Personal stories and feelings reveal the profound impact that this skin disorder can have on well-being.
By focusing on the patient's viewpoint, healthcare providers can better grasp the challenges faced. It improves communication and fosters more tailored treatment strategies. Involving patients in their own care plan leads to improved satisfaction. Their experiences also highlight the necessity of education and awareness regarding idiopathic urticaria.
Quality of Life Impacts
Quality of life is a multifaceted concept, significantly influenced by idiopathic urticaria. Individuals may experience persistent itching, swelling, and discomfort. These physical symptoms can disrupt sleep, social interactions, and work life. Anxiety often accompanies these challenges, leading to frustration and stress.
Patients report feelings of embarrassment due to visible hives. This can result in social withdrawal and decreased self-esteem. The unpredictability of flare-ups adds another layer of difficulty. Individuals might avoid situations where symptoms could worsen. This avoidance can limit opportunities and life experiences.
Assessing the overall impact of idiopathic urticaria on life involves considering both emotional and physical aspects. It is not just about the skin but the mind as well. Effective communication of these challenges can promote understanding and compassion from others.
Coping Mechanisms Employed
Patients utilize various coping mechanisms to manage idiopathic urticaria. These strategies vary widely among individuals, shaped by personal experiences and backgrounds.
Common practices include:
- Stress Management: Techniques such as meditation, yoga, and exercise can help reduce stress levels. Managing stress is crucial as it often exacerbates symptoms.
- Dietary Adjustments: Some patients report success with specific dietary changes. Identifying potential food triggers helps in managing flare-ups. Keeping a food diary can be beneficial to track correlations.
- Medication Adherence: Regular use of antihistamines or prescribed treatments is vital for symptom control. Understanding how and when to take medications greatly affects their effectiveness.
- Support Systems: Engaging with friends, family, or support groups provides emotional relief. Sharing experiences fosters a sense of community and understanding.
"Dealing with idiopathic urticaria feels like an uphill battle, but connecting with others made a difference. It helps to know I am not alone."
The End and Future Directions
Understanding idiopathic urticaria is critical in both clinical practice and patient experience. This condition can severely affect the quality of life, leading to physical discomfort and psychological distress. Thus, recognizing the symptoms and their implications is essential for effective management. The conclusion drawn from this exploration highlights the necessity to inform patients and healthcare providers about the various manifestations and potential triggers of idiopathic urticaria. Moreover, it emphasizes the importance of a patient-centered approach in treatment, tailored to individual needs, which can significantly enhance outcomes.
Moreover, as the field of dermatology continues to evolve, it is vital to embrace future directions that refine research and treatment methodologies. Emerging studies could reveal novel insights into the etiology and pathophysiology of this disorder. Continuous efforts are needed to build robust clinical guidelines that integrate findings from recent research. This can lead to a clearer understanding of how different factors contribute to the prevalence of symptoms in varying demographics.
A holistic approach to idiopathic urticaria may involve multidisciplinary collaboration among professionals across dermatology, immunology, and mental health. Such collaboration could pave the way for innovative treatments that not only address the physical symptoms but also consider the mental health aspects associated with chronic illnesses.
Ultimately, further exploration is warranted to close the current gaps in knowledge surrounding this condition. This project aims to enhance awareness, assist in elucidating underlying complexities, and foster a clear pathway towards more effective treatments and management strategies.
Summary of Key Points
- Idiopathic urticaria presents significant challenges, impacting patients' lives both physically and psychologically.
- Recognizing symptoms and understanding triggers are vital for management and treatment efforts.
- Future research should focus on the etiology and pathophysiology of the condition to inform clinical practices better.
- A multidisciplinary approach can aid in the comprehensive management of the disorder, considering both physical and mental health aspects.
Research Gaps and Opportunities
Despite the strides made in understanding idiopathic urticaria, several gaps remain:
- The exact etiology and pathogenesis are not fully understood, requiring more targeted studies.
- There is limited research examining the psychosocial impact of idiopathic urticaria, which could offer valuable insights into patient care.
- Many treatment protocols are derived from anecdotal evidence rather than comprehensive clinical trials, indicating a need for robust, empirical research.
Opening dialogues among researchers, healthcare professionals, and patients can uncover new opportunities to address these challenges. Addressing the gaps will not only enhance the existing body of knowledge but also foster innovative approaches to treatment and management.







